單壁碳納米管M2013L2 Ossila碳納米管M2012L1 進(jìn)口碳納米管M2013L1
單壁碳納米管M2013L2 Ossila碳納米管M2012L1 進(jìn)口碳納米管M2013L1Ossila廠家直接訂貨、原裝正品、交期準(zhǔn)時、歡迎新老客戶!!!
只用于動物實驗研究等
Product List
All our SWNTs come packed as dry powders, which can be dispersed within the user's solvent of choice.
Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Powders
| Product code | M2012L1 | M2013L1 | M2013L2 |
| Outer Diameter | < 2 nm | < 2 nm | < 2 nm |
| Length | 5-50 μm | 4-20 μm | 5-30 μm |
| Specific Surface Area | 500-700 m2.g-1 | 400-1000 m2.g-1 | 400-1000 m2.g-1 |
| Purity | > 90% | > 95% | > 95% |
| MSDS | |||
| Sale Quantities | 1 g | 250 mg, 500 mg, 1 g | |
| Packaging Information | Light-resistant bottle | ||
*For larger orders, please us to discuss prices.
Functionalised Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Powders
| Product code | M2014L1 | M2015L1 |
| Outer Diameter | < 2 nm | < 2 nm |
| Length | 5-30 μm | 5-30 μm |
| Specific Surface Area | 380 m2.g-1 | 380 m2.g-1 |
| Functional Group | COOH | OH |
| Functional Group Wt.% | ~ 3% | ~ 4% |
| Purity | > 90% | > 90% |
| MSDS | ||
| Sale Quantities | 250 mg, 500 mg, 1 g | |
| Packaging Information | Light-resistant bottle | |
單壁碳納米管M2013L2 Ossila碳納米管M2012L1 進(jìn)口碳納米管M2013L1
*For larger orders, please us to discuss prices.
What are Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes?
SWNTs are sheets of graphene that have been rolled up to form a long hollow tube, with walls a single atom thick. The existence of thin, hollow carbon tubes has been known about since their first observations by L. V. Radushkevich and V. M. Lukyanovich in 1952, however, the first observations of SWNTs themselves were not until 1976 when M. Endo synthesised a series of hollow carbon tubes via chemical vapour-growth. Wider interest in these low-dimensional materials did not occur until 1991, when two articles were independently published by: i) S. Iijima on the fabrication of multi-walled carbon nanotubes via arc discharge, and ii) J. W. Mintire, B. I. Dunlap, and C. T. White on the predicted properties of SWNTs. The combination of a simple method for producing SWNTs and the potentially extraordinary properties they exhibit kick-started the growth of a wider research community into carbon nanotubes. 單壁碳納米管M2013L2 Ossila碳納米管M2012L1 進(jìn)口碳納米管M2013L1 Much like graphene, SWNTs have properties that differ considerably to those of bulk carbon (e.g. graphite). The mechanical properties vary significantly depending upon the axis you are measuring with nanotubes having extremely high Youngs Moduli (Up to 1TPa) and tensile strength (Up to 100 GPa) along the longitudinal axis. Along the radial axis, these values are a few orders of magnitude lower. | |||
The electrical properties of carbon nanotubes are dependent upon the orientation of the lattice. The lattice orientation is given by two parameters (n, m). The image to the right shows how the n and m orientations relate to the longitudinal axis of the nanotube and the rotational axis. There are typically three types of nanotubes that can form, these are: the armchair (where n = m), zig-zag (n=x, m=0), and chiral (n=x, m=y). Carbon nanotubes can exhibit either metallic properties or semiconducting properties, depending upon the orientation of the lattice. Zig-zag and armchair carbon nanotubes exhibit metallic properties, whilst chiral nanotubes can be either metallic or semiconducting depending upon the difference between the n and m units. In addition to this ability to exhibit both metallic and semiconducting electronic structures carbon nanotubes offer exceptional charge carrier mobilities, this is due to the combination of the delocalisation of electrons across the lattice and the small dimensions in the radial axis constraining movement of charge carriers along the longitudinal axis of the tubes. |
How the lattice parameters relate to the physical structure of carbon nanotubes. | ||
In addition to the electronic and mechanical properties of SWNTs, the thermal properties of these materials exhibit extreme anisotropy. Along the length of the tube, thermal conductivity can be up to 9 times higher than materials such as copper. However - across the radial axis, the thermal conductivity can be 250 times lower than that of copper. Much like its electrical and mechanical properties, SWNT's thermal properties can be severely affected by the presence of defects along the nanotube length. The presence of these defects lead to phonon scattering. When these defects interact with low frequency phonons, scattering can occur - reducing the thermal conductivity. At the time being, there are limited commercial applications for SWNTs. They are used in composite materials as a method of improving mechanical strength. One of the current limiting factors in improving the range of applications of carbon nanotubes is the ordering of nanotube structure. Current commercial applications utilise disordered bundles of nanotubes, and these bundles have a significantly lower performance than that of individual nanotubes. Potential future uses for carbon nanotubes could be seen in areas such as transparent conducting layers for use in display technologies, conductive wires for nanoelectronics, electrodes in thin-film electronic devices, carbon nanotube yarns for ultra-strong fabrics, thermal management systems, advanced drug delivery systems and many other wide-ranging fields. | |||
Dispersion Guides
SWNTs are insoluble as prepared. However, through the use of surfactants and ultrasonic probes, it is possible to disperse and suspend small concentrations of nanotubes. For dispersing in aqueous solutions, we recommend the use of sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate if an ionic surfactant is suitable. If a nonionic surfactant is needed, we recommend surfactants with high molecular weights.
- Weigh out the desired amount of carbon nanotubes.
- Mix together your solvent and surfactant of choice at the desired surfactant concentration; this should be below the critical micelle concentration of the surfactant.
- Add the solvent-surfactant mix to the dry powder and shake vigorously to mix.
- Either place an ultrasonic probe into the solution, or place the solution into an ultrasonic bath.
- Be careful about the length of time and power used - because damage to the carbon nanotubes can occur, shortening their average length.
- The resulting solution will be a mixture of suspended SWNT's and bundles of SWNT's, further sonication will help break up the bundles.
- To separate out the individual nanotubes in solution from the bundles, the solution should be placed into a centrifuge. If the solution is centrifuged for a longer time and/or at a higher speed, the smaller bundles will be removed, narrowing the distribution of suspended nanotubes.
For functionalised SWNTs, it is possible to disperse them without the use of any surfactants. However, the total concentration of dispersed nanotubes will be lower. A maximum of 0.1mg/ml can be achieved for -COOH and -OH.
Technical Data
General Information
| CAS number | 7440-44-0 |
| Chemical formula | CxHy |
| Recommended Dispersants | DI Water, DMF, THF, Ethanol, Acetone |
| Synonyms | Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes, Single-Wall Carbon Nanotube, Carbon Nanotube, SWNT, CNT |
| Classification / Family | 1D materials, Carbon nanomaterials, Nanomaterials, Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, thin-film electronics |
| Appearance | Black fibrous powder |
Characterisation
 Raman spectra of SWNT samples showing the presence of the G+ and G- band, the D band, and also the radial breathing mode peaks.
Raman spectra of SWNT samples showing the presence of the G+ and G- band, the D band, and also the radial breathing mode peaks.
 TEM image of an individual SWNT.
TEM image of an individual SWNT.
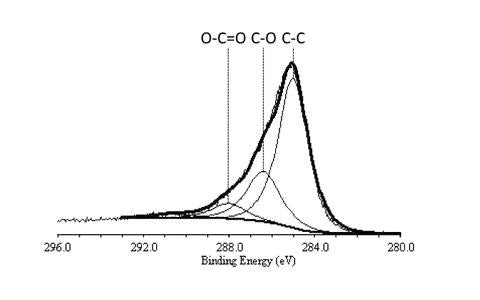 XPS spectra of the C1s peak for functionalized carbon nanotubes showing the presence of C-C, C-O, and O-C=O bonds.
XPS spectra of the C1s peak for functionalized carbon nanotubes showing the presence of C-C, C-O, and O-C=O bonds.
1D Related Products

Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes

Double-Walled Carbon Nanotubes

Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes
Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Publications
- Filamentous Growth of Carbon Through Benzene Decomposition, A. Oberlin et. al., J. Cryst. Growth, 32, 335-349 (1976); DOI: 10.1016/0022-0248(76)90115-9
- Helical Microtubules of Graphitic Carbon, S. Iijima, Nature, 354, 56-58 (1991); doi: 10.1038/354056a0
- Are Fullerene Tubules Metallic?, J. W. Mintire et al., Phys. Rev. Lett., 68, 631 (1992); doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.68.631
- Large-Scale Production of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes by the Electric-Arc Technique, C. Journetet. al., Nature, 338, 756-758, (1997); doi: 10.1038/41972
- Bandgap Fluorescence from Individual Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes, M. J. O'Connell et. al.,Science, 297, 593-596, (2002); doi: 10.1126/science.1072631
- Atomic Structure and Electronic Properties of Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes Probed by Scanning Tunnel Electron Microscope at Room Temperature.
A. Hassanien et. al. Appl. Phys. Lett., 73, 3839 (1998); DOI: 10.1063/1.122910 - Solution Properties of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. J. Chen et. al., Science, 282, 95-98, (1998); DOI: 10.1126/science.282.5386.95
- Structure-Assigned Optical Spectra of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. S. M. Bachilo et. al., 298, 2361-2366, (2002); DOI: 10.1126/science.1078727
- Carbon Nanotubes—The Route Towards Applications. R. H. Baughman et. al. Science, 297, 787-792, (2002) DOI: 10.1126/science.1060928






 發(fā)送消息
發(fā)送消息